智能合约安全审计平台介绍
by. 北京大学信息安全实验室
项目简介
应用背景
由于链上合约掌管着大量数字资产,且合约一经部署难以更改、交易难以撤销,因此,在区块链安全生态中,针对智能合约的安全攻击尤为突出,难以实时防御。因此,在合约部署前对合约的安全性和功能性进行严格审计至关重要。然而,针对智能合约的审计需求,我们还面对着以下问题:
- 合约审计需要有在区块链、开发语言、执行流程、开发模式等方面足够的专业知识
- 现有合约数量巨大,并且仍在迅速增加。新的安全问题和漏洞模式也在不断出现
- 现有审计服务往往收费高昂且周期较长,出于时间成本和经济成本的考虑难以批量审计
- 自动化工具环境各不相同,输入输出并不统一,且大多疏于维护;已审计过的合约无法沉淀成知识库
本安全审计平台由北京大学和奇安信科技集团股份有限公司合作提供,针对智能合约的安全问题,集成学术界与业界的先进工具,涵盖静态分析、符号执行、模糊测试、形式化验证等多种技术为合约安全提供保障,为您提供便捷的安全审计服务,包括漏洞定位、评级与修补意见,从而防患于未然。
目前,研究团队基于上述关键技术的研究工作已取得多项专利及论文成果并发现以太坊平台多个中高危智能合约零日漏洞。支持多种生态场景下的合约审计,包括公链与联盟链上solidity、go源代码或字节码,适配新老版本。已审计的合约的信息、特征及审计结果将会被持久化到合约仓库,及时反馈到审计系统进行回查,也会被用于工具的持续优化。
智能合约漏洞检测
本项目支持针对Ethereum系统solidity智能合约和Hyperledger Fabric系统Go链码的已知安全漏洞的检测和定位。用户上传智能合约文件,系统返回的检测报告,包含漏洞类型、所在位置、漏洞描述及修改建议。
针对solidity智能合约
覆盖漏洞如下:
| 序号 | 检测类型 | 检测描述 | 等级 | 可信度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | abiencoderv2-array | Storage abiencoderv2 array | High | High |
| 2 | arbitrary-send-erc20 | transferFrom uses arbitrary from | High | High |
| 3 | array-by-reference | Modifying storage array by value | High | High |
| 4 | incorrect-shift | The order of parameters in a shift instruction is incorrect. | High | High |
| 5 | multiple-constructors | Multiple constructor schemes | High | High |
| 6 | name-reused | Contract’s name reused | High | High |
| 7 | protected-vars | Detected unprotected variables | High | High |
| 8 | public-mappings-nested | Public mappings with nested variables | High | High |
| 9 | rtlo | Right-To-Left-Override control character is used | High | High |
| 10 | shadowing-state | State variables shadowing | High | High |
| 11 | suicidal | Functions allowing anyone to destruct the contract | High | High |
| 12 | uninitialized-state | Uninitialized state variables | High | High |
| 13 | uninitialized-storage | Uninitialized storage variables | High | High |
| 14 | unprotected-upgrade | Unprotected upgradeable contract | High | High |
| 15 | codex | Use Codex to find vulnerabilities. | High | Low |
| 16 | arbitrary-send-erc20-permit | transferFrom uses arbitrary from with permit | High | Medium |
| 17 | arbitrary-send-eth | Functions that send Ether to arbitrary destinations | High | Medium |
| 18 | controlled-array-length | Tainted array length assignment | High | Medium |
| 19 | controlled-delegatecall | Controlled delegatecall destination | High | Medium |
| 20 | delegatecall-loop | Payable functions using delegatecall inside a loop | High | Medium |
| 21 | msg-value-loop | msg.value inside a loop | High | Medium |
| 22 | reentrancy-eth | Reentrancy vulnerabilities (theft of ethers) | High | Medium |
| 23 | storage-array | Signed storage integer array compiler bug | High | Medium |
| 24 | unchecked-transfer | Unchecked tokens transfer | High | Medium |
| 25 | weak-prng | Weak PRNG | High | Medium |
| 26 | domain-separator-collision | Detects ERC20 tokens that have a function whose signature collides with EIP-2612’s DOMAIN_SEPARATOR() | Medium | High |
| 27 | enum-conversion | Detect dangerous enum conversion | Medium | High |
| 28 | erc20-interface | Incorrect ERC20 interfaces | Medium | High |
| 29 | erc721-interface | Incorrect ERC721 interfaces | Medium | High |
| 30 | incorrect-equality | Dangerous strict equalities | Medium | High |
| 31 | locked-ether | Contracts that lock ether | Medium | High |
| 32 | mapping-deletion | Deletion on mapping containing a structure | Medium | High |
| 33 | shadowing-abstract | State variables shadowing from abstract contracts | Medium | High |
| 34 | tautology | Tautology or contradiction | Medium | High |
| 35 | write-after-write | Unused write | Medium | High |
| 36 | boolean-cst | Misuse of Boolean constant | Medium | Medium |
| 37 | constant-function-asm | Constant functions using assembly code | Medium | Medium |
| 38 | constant-function-state | Constant functions changing the state | Medium | Medium |
| 39 | divide-before-multiply | Imprecise arithmetic operations order | Medium | Medium |
| 40 | reentrancy-no-eth | Reentrancy vulnerabilities (no theft of ethers) | Medium | Medium |
| 41 | reused-constructor | Reused base constructor | Medium | Medium |
| 42 | tx-origin | Dangerous usage of tx.origin | Medium | Medium |
| 43 | unchecked-lowlevel | Unchecked low-level calls | Medium | Medium |
| 44 | unchecked-send | Unchecked send | Medium | Medium |
| 45 | uninitialized-local | Uninitialized local variables | Medium | Medium |
| 46 | unused-return | Unused return values | Medium | Medium |
| 47 | incorrect-modifier | Modifiers that can return the default value | Low | High |
| 48 | shadowing-builtin | Built-in symbol shadowing | Low | High |
| 49 | shadowing-local | Local variables shadowing | Low | High |
| 50 | uninitialized-fptr-cst | Uninitialized function pointer calls in constructors | Low | High |
| 51 | variable-scope | Local variables used prior their declaration | Low | High |
| 52 | void-cst | Constructor called not implemented | Low | High |
| 53 | calls-loop | Multiple calls in a loop | Low | Medium |
| 54 | events-access | Missing Events Access Control | Low | Medium |
| 55 | events-maths | Missing Events Arithmetic | Low | Medium |
| 56 | incorrect-unary | Dangerous unary expressions | Low | Medium |
| 57 | missing-zero-check | Missing Zero Address Validation | Low | Medium |
| 58 | reentrancy-benign | Benign reentrancy vulnerabilities | Low | Medium |
| 59 | reentrancy-events | Reentrancy vulnerabilities leading to out-of-order Events | Low | Medium |
| 60 | timestamp | Dangerous usage of block.timestamp | Low | Medium |
| 61 | assembly | Assembly usage | Informational | High |
| 62 | assert-state-change | Assert state change | Informational | High |
| 63 | boolean-equal | Comparison to boolean constant | Informational | High |
| 64 | deprecated-standards | Deprecated Solidity Standards | Informational | High |
| 65 | erc20-indexed | Un-indexed ERC20 event parameters | Informational | High |
| 66 | function-init-state | Function initializing state variables | Informational | High |
| 67 | low-level-calls | Low level calls | Informational | High |
| 68 | missing-inheritance | Missing inheritance | Informational | High |
| 69 | naming-convention | Conformity to Solidity naming conventions | Informational | High |
| 70 | pragma | If different pragma directives are used | Informational | High |
| 71 | redundant-statements | Redundant statements | Informational | High |
| 72 | solc-version | Incorrect Solidity version | Informational | High |
| 73 | unimplemented-functions | Unimplemented functions | Informational | High |
| 74 | unused-state | Unused state variables | Informational | High |
| 75 | costly-loop | Costly operations in a loop | Informational | Medium |
| 76 | dead-code | Functions that are not used | Informational | Medium |
| 77 | reentrancy-unlimited-gas | Reentrancy vulnerabilities through send and transfer | Informational | Medium |
| 78 | similar-names | Variable names are too similar | Informational | Medium |
| 79 | too-many-digits | Conformance to numeric notation best practices | Informational | Medium |
| 80 | constable-states | State variables that could be declared constant | Optimization | High |
| 81 | external-function | Public function that could be declared external | Optimization | High |
| 82 | immutable-states | State variables that could be declared immutable | Optimization | High |
| 83 | var-read-using-this | Contract reads its own variable using this | Optimization | High |
针对Go链码
目前正处于开发中,开发进度将及时在此处同步。检测原理如图:

预计覆盖漏洞如下:
| 序号 | 漏洞名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 全局变量及字段声明 | 不同节点中全局变量和字段值可能不同 |
| 2 | 随机数与时间戳依赖 | 执行路径及结果不应依赖随机数和时间戳 |
| 3 | range over map | 读取键值顺序随机,可能会导致结果不确定 |
| 4 | gorountine | 链码中不鼓励使用并发 |
| 5 | 区块链引入的不确定性 | web服务,系统命令,外部文件访问,第三方库 |
| 6 | 幻影读 | 部分查询函数返回的结果不能用于更新账本 |
| 7 | 跨通道链码调用 | 不能通过调用其他通道上的链码提交数据 |
| 8 | 写后读 | 不能在同一个交易中更新并读取同一个key值 |
| 9 | 隐私泄露 | 隐私数据不应影响链码执行路径,不应作为方法返回值 |
| 10 | 溢出 | 未受保护的数值计算 |
智能合约形式化验证
本项目提供适用于组合交易场景的Solidity智能合约形式化验证的方法,用户将需要验证的功能语义插入到智能合约中,最终检验合约是否满足这些功能语义。具体而言,该功能基于以太坊智能合约的Solidity源代码,添加合约约束,包括组合交易场景中的跨函数和跨合约约束,再将添加合约约束后的Solidity源代码转换为中间验证语言(如Boogie)中相对应的类型、语句、表达式和约束,通过验证器自动地对中间验证语言文件进行形式化验证。检测原理如图所示:
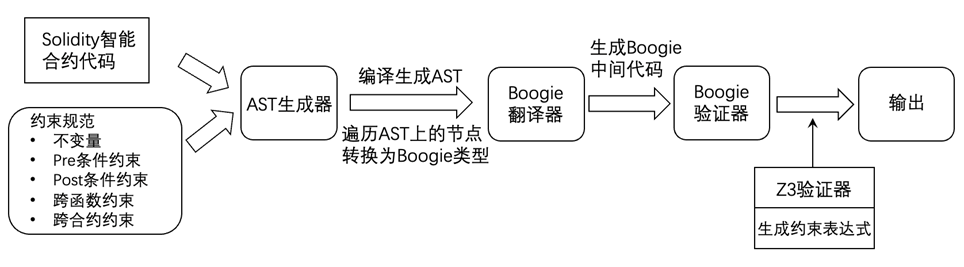
输入说明
功能约束语句包括两大类,第一类是源代码中自带的require、assert语句,放在函数体内,第二类是注释的形式,放在合约或者函数体前,以”/// @”开头。本发明中,注释类型的合约约束包括以下几类:
-
合约层的不变量约束。 在合约开头添加对合约内状态变量的约束,保证合约执行过程中该变量保持不变。合约中的每个public属性的函数会继承该约束,转化为该函数的pre条件和post条件,也就是函数在进入前和执行后都需要验证该状态变量的不变性。合约层的不变量约束形式为:
///@notice\ invariant\ <Expression> -
函数层的pre条件约束和post条件约束。 pre条件是进入函数时需要满足的条件,post条件是函数执行后需要满足的条件。pre条件约束形式为:
///\ @notice\ precondition\ <Expression>post条件约束形式为
///\ @notice\ postcondition\ <Expression> - 循环不变量约束。 在循环体前添加状态变量的不变性约束,保证整个循环执行过程中该状态变量的不变性。循环不变量约束形式与合约层的不变量约束形式相同。
-
跨函数约束。 多笔交易场景下的对函数关系的约束,添加在合约开头。函数间的关系包括:执行的先后次序、互斥关系。函数的先后次序指某个函数执行之后才可以执行另外一个函数,否则另外一个函数的pre条件约束将无法被满足。先后次序的约束形式为:
///\ @notice\ invariant\ <函数A ==>函数B>函数的互斥关系指两个函数不能同时被调用,否则任何一个函数的pre约束将无法被满足。互斥关系的约束形式为:
///\ @notice\ invariant\ <函数A∥函数B> - 跨合约约束。 多个合约场景下的约束。跨合约场景下包含多个合约,需要在其中一个合约中添加其他合约的函数或状态变量的约束。有时我们需要调用第三方合约库中的函数,但并不知道这些合约的功能正确性,因此可以在本合约中添加对这些第三方合约的约束,以验证是否满足我们想要的功能属性。这些约束包括上述的不变量约束、pre/post条件约束、跨函数约束。约束的书写形式与位置与本合约自身的约束书写形式与位置相同,调用另一个合约的状态变量或者函数使用“.”的形式,“.”的左边是其他合约的合约名,右边是其他合约中的状态变量名与函数名,即“ContractName.Variable”或者“ContractName.Function”。
- 数组或映射的总和。 除了对状态变量的值进行直接约束,还可以对数组(array)或者映射(mapping)的总和值进行约束。由于以太坊智能合约中经常涉及账户余额的增减操作,因此对转账的账户进行余额检查必不可少,最直接的方式就是检查相互转账的账户余额总和是否保持不变。本发明提供内置函数verifier_sum_type(),type为数组或者映射的具体数据类型,可以计算整个数组或者映射的总和值,这样verifier_sum_type()实际上和其他普通状态变量相同,也可以作为不变量或者放在pre/post条件中进行约束。
输出说明
验证结果包含OK、Error两种类型,每个合约的每个函数都是一行,首先输出合约名与函数名,然后输出验证结果。例如:
C1: funcA: OK
若验证不通过,则输出信息形式如下:
C1: funcA: Error
--{position information}: Postcondition “postcondition expression” might not hold at end of function
Position information是不满足约束的源代码位置,postcondition expression是输入的约束信息,即会追溯到出错的位置以及约束信息,并且输出。
智能合约未知漏洞挖掘
受服务器成本问题,该功能暂时不开放试用。 不同于人工设计规则、硬编码特征的检测方法,机器学习尤其是深度学习方法提供了自动挖掘模式特征的能力,深度学习方法直接从输入的源码数据中提取上下文特征而不需要人工预定义策略和特征,因此可用于发觉代码中未知的潜在威胁。本审计平台提供基于机器学习的智能合约安全漏洞检测功能,用于检测以太坊智能合约中的潜在威胁。
具体而言,该功能将智能合约漏洞检测问题建模为一个分类问题并且实现了一个端到端的检测方法,首先从源代码构建的抽象语法树中提取相关合约片段,然后通过深度学习编码器抽取得到模式,并生成一个表达漏洞语义信息的语义嵌入向量。将这个语义嵌入向量作为后续全连接检测网络模型的输入,检测网络模型最后的softmax层会输出样本属于“包含漏洞类”的概率。
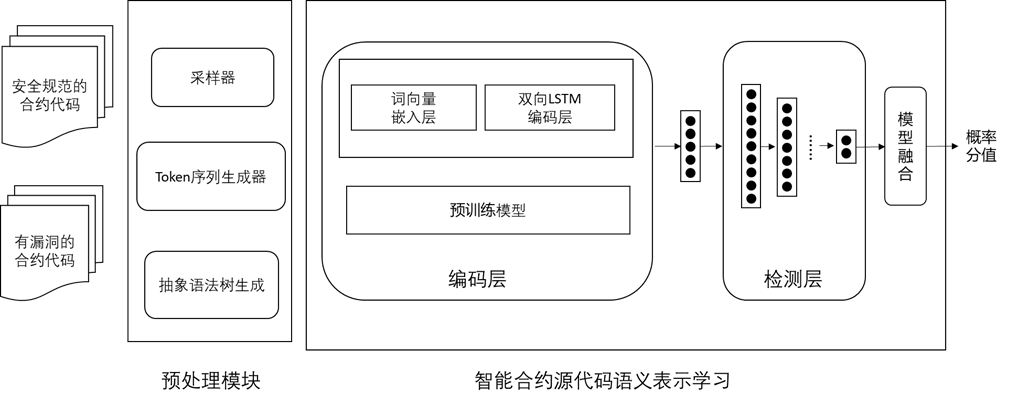
- 测试集来源:https://smartbugs.github.io/
团队成果展示
论文成果
在区块链领域国内外知名会议/期刊累计发表论文 37篇 。
| 年份 | 论文名称 | 发表刊物 |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | Smifier: A Smart Contract Verifier for Composite Transactions | SEKE |
| 2022 | RegLang:一种面向监管的智能合约编程语言 | 计算机科学 |
| 2022 | 基于区块链的无证书签密方案 | 计算机与现代化 |
| 2021 | FASTBLOCK: Accelerating Blockchains via Hardware Transactional Memory | ICDCS |
| 2021 | TrustCross : Enabling Confidential Interoperability across Blockchains Using Trusted Hardware | ICBTA |
| 2021 | 应用区块链的多接收者多消息签密方案 | 软件学报 |
| 2021 | 群智感知中基于区块链的带时效签密方案 | 计算机学报 |
| 2021 | 区块链数据安全服务综述 | 软件学报 |
| 2021 | TBFT: Efficient Byzantine Fault Tolerance Using Trusted Execution Environment | ICC |
| 2021 | Blockchain-based Multi-recipient Multi-message Signcryption Scheme | Journal of Software |
| 2021 | 数字货币的安全和发展 | 中国信息安全 |
| 2021 | 基于区块链的学历证书可信认证系统 | 计算机时代 |
| 2020 | Kaya: A Testing Framework for Blockchain-based Decentralized Applications | ICSME |
| 2020 | Studying gas exceptions in blockchain-based cloud applications | Journal of Cloud Computing |
| 2020 | EShield: Protect Smart Contracts against Reverse Engineering | ISSTA |
| 2020 | Mining DApp Repositories: Towards In-Depth Comprehension and Accurate Classification | SEKE |
| 2020 | 智能合约安全漏洞检测技术研究 | 保密科学技术 |
| 2020 | 区块链隐私保护技术综述 | 保密科学技术 |
| 2020 | 智能合约及基础软硬件安全解读 | 金融电子化 |
| 2020 | 基于中国剩余定理的区块链投票场景签名方案 | 计算机应用研究 |
| 2020 | 区块链性能扩展与安全研究 | 信息网络安全 |
| 2019 | EasyFlow: keep ethereum away from overflow | ICSE |
| 2019 | Guided, automated testing of blockchain-based decentralized applications | ICSE |
| 2019 | Towards Automated Migration for Blockchain-based Decentralized Application | ICPC |
| 2019 | Understanding Out of Gas Exceptions on Ethereum | BlockSys |
| 2019 | Performance Analysis of the Libra Blockchain: An Experimental Study | HotICN |
| 2019 | 国产密码体系在区块链中的应用与挑战 | 中国信息安全 |
| 2019 | 区块链在政务服务与监管科技领域的应用、挑战与创新 | 软件和集成电路 |
| 2019 | AuthLedger: A Novel Blockchain-based Domain Name Authentication Scheme | ICISSP |
| 2019 | Towards automated testing of blockchain-based decentralized applications | ICPC |
| 2019 | Finding concurrency exploits on smart contracts | ICSE Companion |
| 2018 | Reguard: finding reentrancy bugs in smart contracts | ICSE Companion |
| 2018 | S-gram: towards semantic-aware security auditing for Ethereum smart contracts | ASE |
| 2018 | EClone: detect semantic clones in Ethereum via symbolic transaction sketch | ESEC/FSE |
| 2018 | Analysis of Man-In-The-Middle of Attack on Bitcoin Address | ICETE |
| 2018 | 一种整数上的PACDP全同态加密改进 | 控制工程 |
| 2016 | 加密数据上的计算密码学技术研究综述 | 计算机应用研究 |
专利成果
在区块链领域累计申请专利 16 项,其中授权专利 7 项。
| 专利状态 | 公开年份 | 专利名称 | 专利号/申请号 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 申请专利 | 2022 | 一种Fabric区块链系统智能合约的安全分析检测方法 | CN202210029433.4 |
| 申请专利 | 2021 | 一种基于区块链的数字函证平台及方法 | CN202110171263.9 |
| 申请专利 | 2020 | 一种智能合约安全增强方法 | CN202010211696.8 |
| 申请专利 | 2020 | 一种针对智能合约行为的监管方法 | CN202010211697.2 |
| 申请专利 | 2020 | 一种基于共识参与度和交易活跃度的改进PBFT共识方法 | CN202011152332.3 |
| 申请专利 | 2020 | 一种区块链分片的高效存储重配置方法 | CN202011152333.8 |
| 申请专利 | 2020 | 面向大数据架构与区块链的多源数据处理方法及装置 | CN202010978288.5 |
| 申请专利 | 2020 | 基于智能合约与工作流架构的执法返还系统及方法 | CN202010979863.3 |
| 申请专利 | 2020 | 基于区块链的垂直电商交易平台 | CN202011022370.7 |
| 授权专利 | 2022 | 基于深度学习的以太坊智能合约安全漏洞检测方法与系统 | CN202210029518.2 |
| 授权专利 | 2022 | 一种适用于组合交易的智能合约形式化验证方法及系统 | CN202210029440.4 |
| 授权专利 | 2018 | 一种SM2公钥密码的数字签名快速生成方法 | CN201811323155.3 |
| 授权专利 | 2018 | 一种两方SM2数字签名生成方法 | CN201811381814.9 |
| 授权专利 | 2018 | SM3密码杂凑算法的并行化优化方法 | CN201811323148.3 |
| 授权专利 | 2016 | 基于组合公钥的密码学货币地址在线生成方法 | CN201610938140.2 |
| 授权专利 | 2012 | 一种抵御冷启动攻击的公钥密码实现方法 | CN201210171306.4 |
零日漏洞
累计在以太坊平台发现 15 个智能合约 零日漏洞 ,含多个中危、高危漏洞。














